Physics-augmented ML for modeling nonlinear 3D beams
2024/12/04
In our latest publication, we develop physics-augmented neural networks for material modeling of 3D beams that exhibit nonlinear, hyperelastic material behavior. So far either only linear elastic materials could be considered, or computationally involving FE²-type approaches had to be used.
Congratulations to our doctoral researcher Jasper Schommartz on the publication of his first journal article in Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering! Thanks also to Dominik K. Klein and Juan C. Alzate Cobo for their contributions!
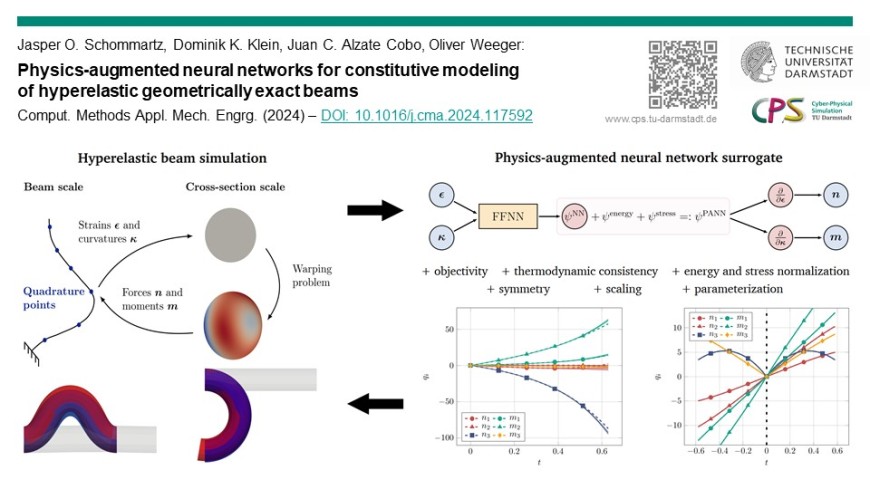
In this work, we present neural network-based constitutive models for hyperelastic geometrically exact beams. The proposed models are physics-augmented, i.e., formulated to fulfill important mechanical conditions by construction, which improves accuracy and generalization. This enables efficient constitutive surrogate modeling for geometrically exact beams with nonlinear material behavior and cross-sectional deformation, which otherwise would require computationally much more expensive methods. The models are calibrated and tested with data generated for beams with circular and ring-shaped hyperelastic deformable cross-sections at varying inner and outer radii, showing excellent accuracy and generalization.
This work is available under Open Access under DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2024.117592


